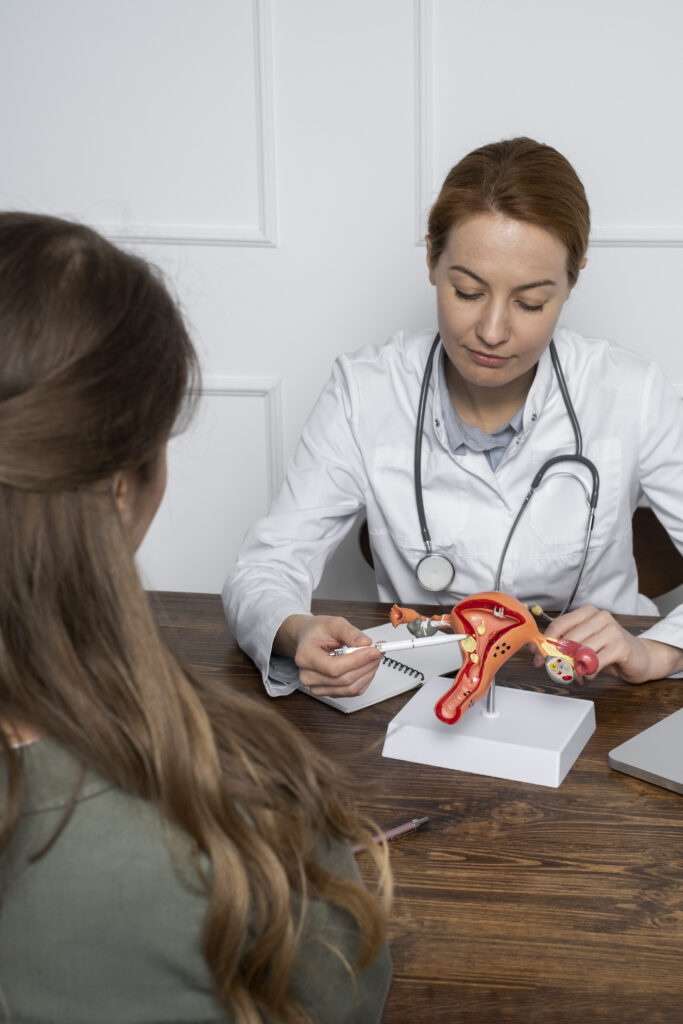
ABOUT GYNAECOLOGY
Gynaecology is the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and care of the female reproductive system. It plays a vital role in promoting overall women’s health—from puberty to post-menopause.
Gynaecology is the medical field focused on the female reproductive system, including the uterus, ovaries, fallopian tubes, cervix and vagina.
It deals with issues like periods, pregnancy, fertility, menopause and conditions such as PCOS, fibroids and infections.
Regular check-ups and screenings help detect problems early and support women’s overall and reproductive health.
Common Gynaecological Diseases & Conditions
1. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder in women of reproductive age, causing excess androgens and irregular periods. Not all have ovarian cysts. Genetics and insulin resistance play major roles.
Symptoms include irregular periods, acne, excess hair, weight gain, hair thinning and oily skin. Insulin resistance raises the risk of diabetes and metabolic issues.
PCOS can affect fertility due to missed ovulation, but many conceive with treatment like lifestyle changes, medications and fertility therapy. Early diagnosis reduces long-term health risks.
2. Endometriosis
Endometriosis is when tissue like the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, causing inflammation, pain and scarring. It commonly affects ovaries, fallopian tubes, pelvic lining and sometimes the bladder or intestines.
The main symptom is pelvic pain, especially during periods. Pain may also occur during sex, urination, or bowel movements. Other symptoms include fatigue, bloating and heavy bleeding. Severity varies and doesn’t always match disease extent.
Infertility is a concern as endometriosis can block tubes or damage organs. Many women conceive with treatment, including pain relief, hormone therapy, or surgery. Early diagnosis improves outcomes and lowers complications.
3. Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids are non-cancerous growths in or on the uterus, influenced by hormones like estrogen. They vary in size and number and can cause discomfort or pressure if large.
Symptoms include heavy bleeding, pelvic pain, frequent urination and lower back pain. Some women have no symptoms and find fibroids during routine exams.
Fibroids may affect fertility or pregnancy depending on size and location. Treatment ranges from medication to surgery. Early detection helps manage symptoms and prevent complications.
4. Ovarian Cysts
5. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) is an infection of the female reproductive organs, often caused by sexually transmitted bacteria like chlamydia or gonorrhea. It affects the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries and can spread if untreated.
Symptoms include lower abdominal pain, fever, unusual discharge, painful urination and pain during sex. Some women have mild or no symptoms, delaying diagnosis and increasing risk of complications like infertility.
Early antibiotic treatment is crucial to prevent damage. Severe cases may need hospitalization or surgery. Regular STI screening, prompt treatment and safe sex help prevent PID and protect reproductive health.
6. Cervical Dysplasia & Cervical Cancer
Early stages usually have no symptoms, so regular Pap smears and HPV tests are essential. Advanced cancer may cause abnormal bleeding or pelvic pain.
Treatment varies by severity and may include monitoring, removal of abnormal cells, or surgery. HPV vaccination and regular screening help prevent and detect cervical cancer early.
7. Menstrual Disorders
Menstrual disorders involve irregularities in cycle timing, flow, or symptoms, such as heavy bleeding, painful periods, or missed periods. These issues can impact daily life and health.
Causes include hormonal imbalances, stress, thyroid problems, PCOS, or fibroids. Symptoms vary and proper diagnosis guides treatment.
Treatment may involve lifestyle changes, medications, or surgery.
Managing these disorders improves quality of life and reduces risks like anemia and infertility.
8. Menopause-Related Issues
Menopause is the permanent end of menstrual periods, usually between ages 45 and 55. Hormonal changes cause physical and emotional symptoms affecting well-being.
Common symptoms include hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, mood swings and sleep problems. Bone loss raises osteoporosis risk and weight gain or skin changes may occur.
Managing menopause includes lifestyle changes, hormone therapy and symptom treatments. Exercise, diet and mental health support improve quality of life and prevent complications.
Common Symptoms to Watch For:

1. Irregular or missed periods.
2. Unusual vaginal discharge or odour.
3. Pelvic or lower abdominal pain.
4. Pain during intercourse.
5. Frequent urination or burning sensation.
6. Unexplained weight gain or hair growth (in PCOS).
7. Bleeding between periods or after menopause.
8. Lumps or pain in the breast.
Counseling and Support
Counseling helps women understand their health and manage emotional challenges related to menstrual, fertility, or sexual issues. It offers a safe space for open discussion and informed decisions.
Support guides women through pregnancy, menopause and chronic conditions. Combining care and support improves overall well-being and quality of life.

Diagnostic Tests in Gynaecology
- Pelvic Examination
- Ultrasound Scan (Abdominal/Transvaginal)
- Pap Smear & HPV Testing
- Hormonal Blood Tests
- Hysteroscopy & Laparoscopy
- Colposcopy (for detailed cervix examination)
- Mammography (for breast screening)
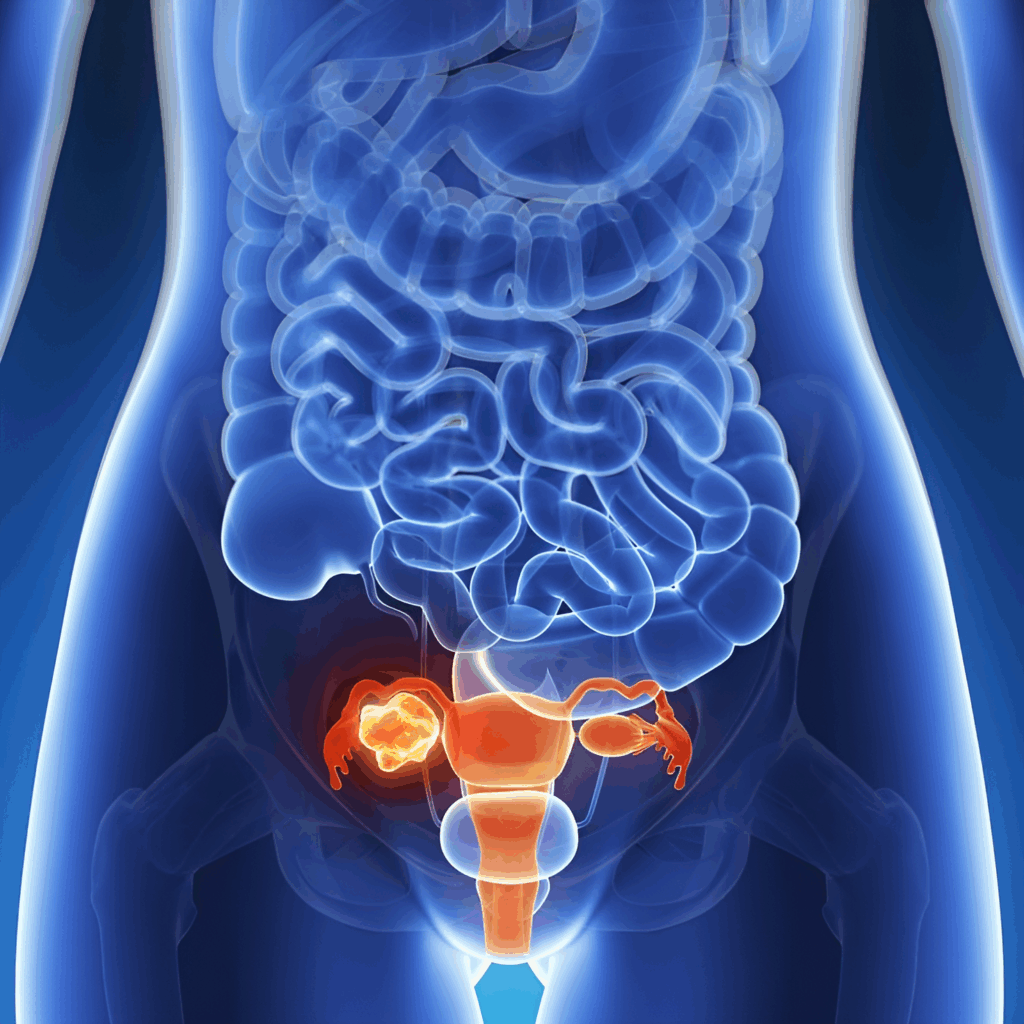
Treatment Options
- Medical Management
- Hormonal therapy, antibiotics, pain management, fertility medications
- Minimally Invasive Surgery
- Laparoscopy, hysteroscopy for cysts, fibroids, endometriosis
- Blood Count (Complete Blood Count, CBC)

Risk Factors Affecting Gynaecological Health
- Family history of reproductive cancers
- Unprotected sex and STIs
- Obesity and poor lifestyle
- Delayed childbirth or no childbirth
- Smoking and alcohol use
- Poor menstrual hygiene
- Early onset of periods or late menopause
Cancer Treatments
Cancer treatment often begins with surgery to remove tumors or affected tissue. Surgery aims to eliminate cancer cells and prevent spread, especially in early stages.
For more advanced cases, chemotherapy and radiotherapy are used. Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells, while radiotherapy uses targeted radiation to shrink tumors and control growth.
Surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy (for advanced cases)
Specific Symptoms to Look Out For
Consult your doctor immediately if you experience any of the following during pregnancy:
- Vaginal bleeding
- Decreased fetal movement
- Lower abdominal pain or cramps
- Watery vaginal discharge (gush or trickle)
- Regular or frequent contractions (tightening in the abdomen)
- Pain or burning during urination
- Changes in vision, including blurred vision
- Persistent headaches
When to See a Gynaecologist
- Period problems
- Planning a pregnancy
- Pain or discomfort in the pelvic area
- Changes in vaginal discharge or bleeding
- Breast lumps or nipple discharge
- Symptoms of menopause
FAQs on Gynaecological Health
At least once a year for a general check-up or earlier if symptoms arise.
From age 21, or earlier if sexually active, as advised by your doctor.
Not always, but persistent irregularity should be evaluated.
Yes—diet, exercise, stress, and sleep have a direct impact on hormonal balance
Clear or white discharge is normal, but changes in color, smell, or quantity can signal infection.
Yes. Conditions like PCOS, endometriosis, and fibroids may impact fertility.
Your health deserves attention: At HERCYCLOPEDIA we provide compassionate and confidential care with state-of-the-art diagnostics and treatment for all gynaecological concerns.
