Most Common Cancers in Women
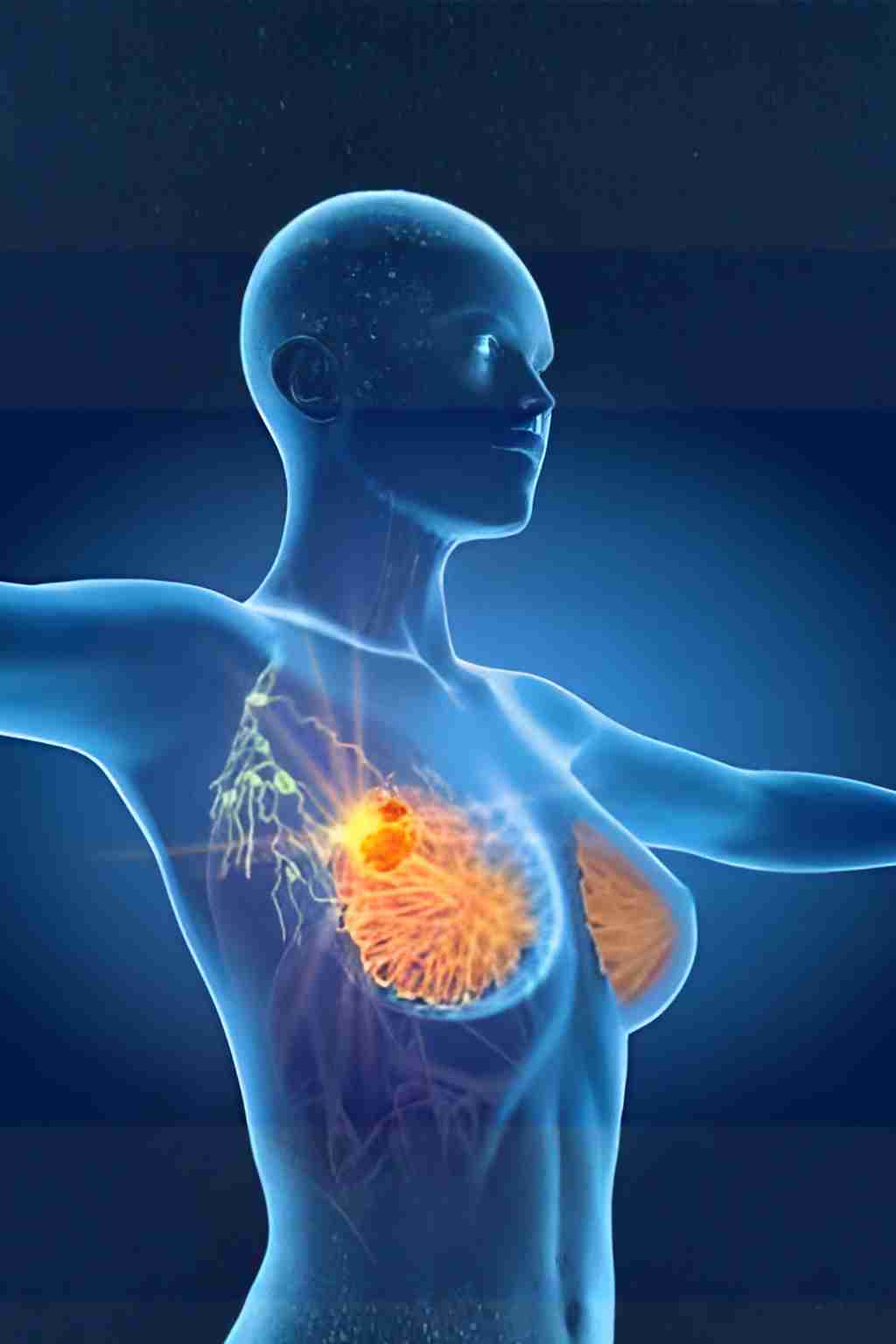
1. Breast Cancer
- Overview: Most frequently diagnosed cancer in women globally.
- Symptoms: Breast lump, nipple inversion/discharge, skin changes.
- Risk Factors: Age, family history (BRCA1/2), obesity, alcohol use, HRT.
2. Cervical Cancer
- Cause: Mostly by persistent high-risk HPV infection.
- Symptoms: Abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, foul-smelling discharge.
- Prevention: HPV vaccination (ages 9–26), Pap smear every 3 years, HPV DNA testing.
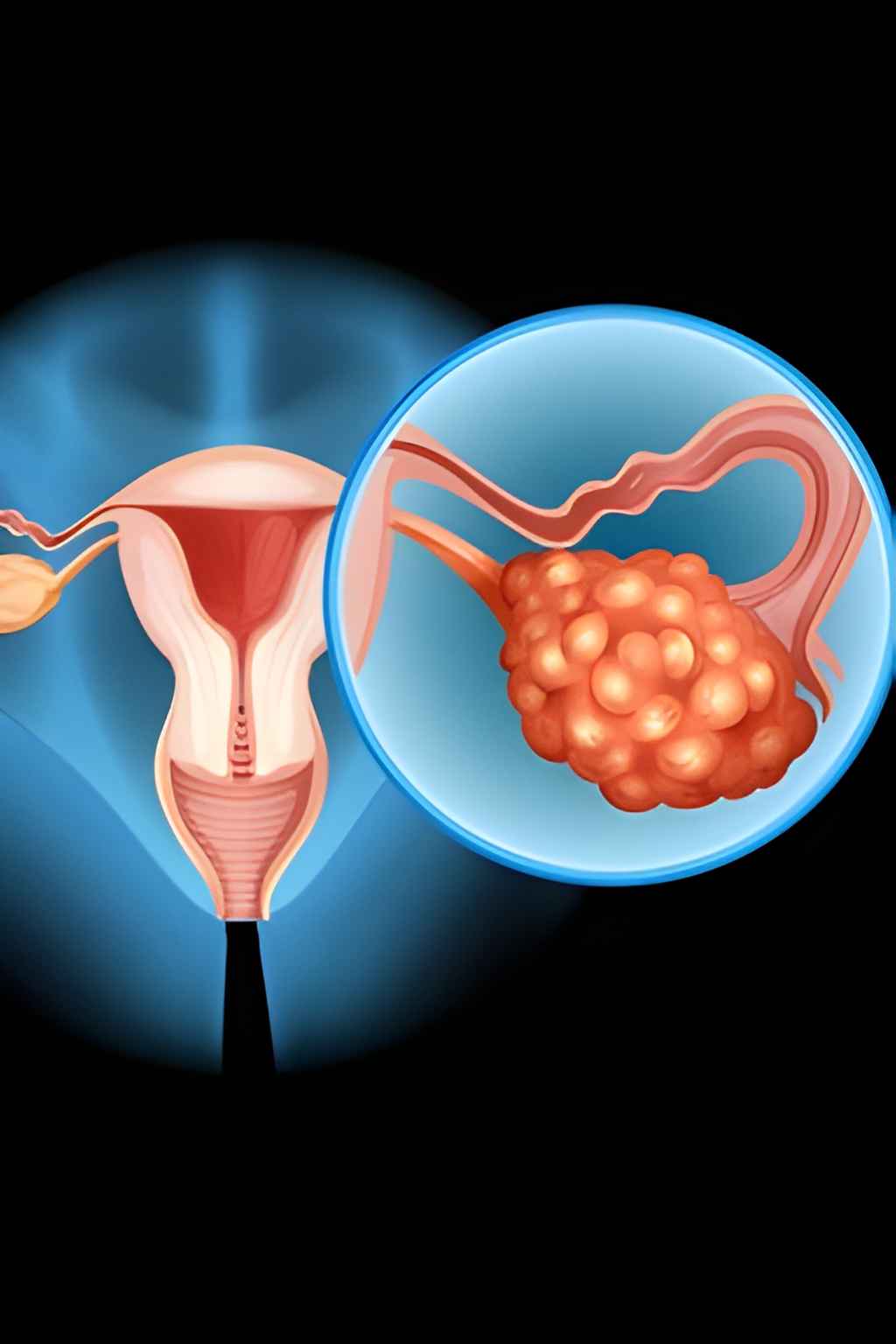
3. Ovarian Cancer
- Symptoms: Bloating, abdominal pain, early satiety, urinary urgency.
- Challenges: Often diagnosed late due to non-specific symptoms.
- Risk Factors: Family history, endometriosis, BRCA mutations.

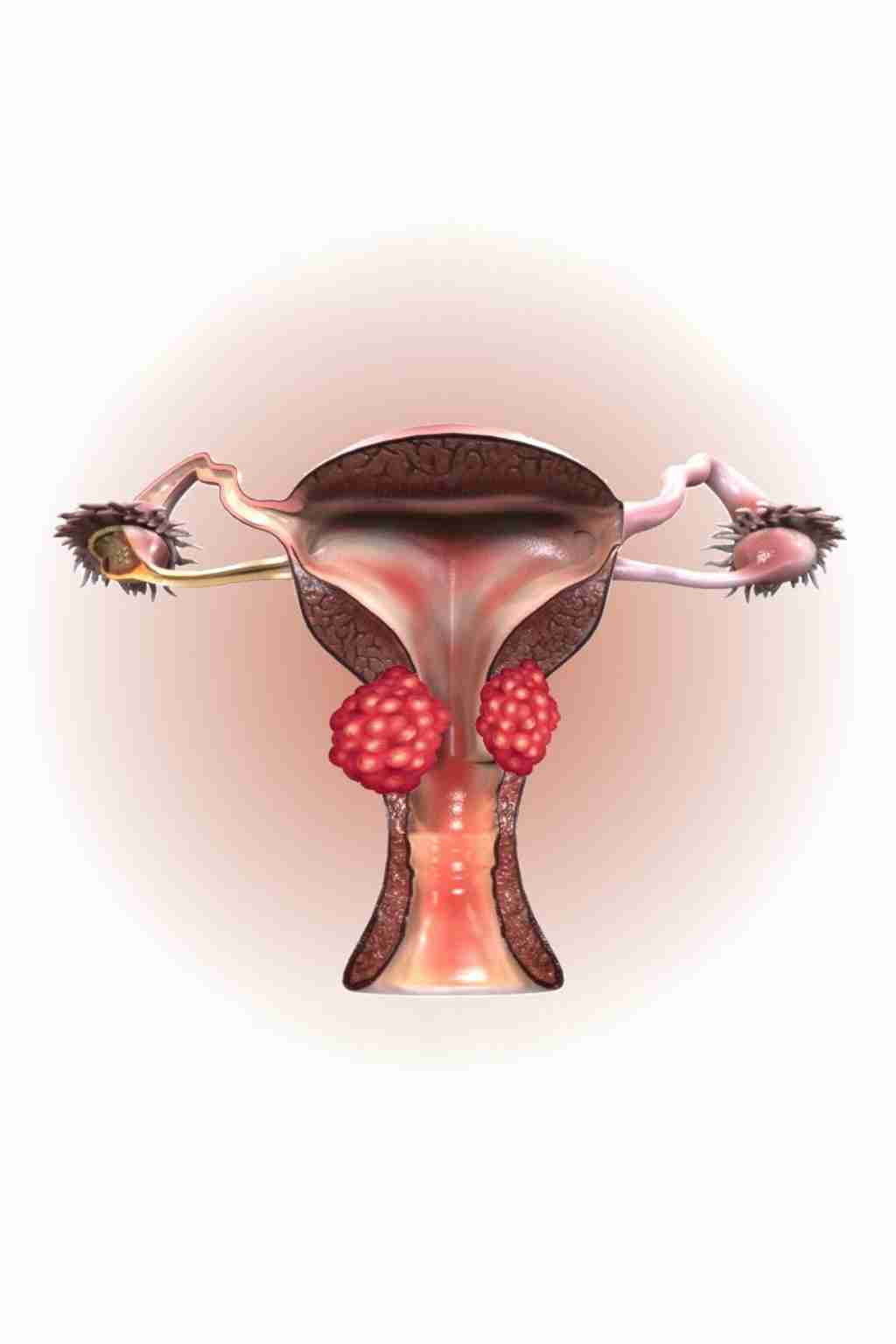
4. Endometrial (Uterine) Cancer
- Symptoms: Postmenopausal bleeding, pelvic discomfort.
- Risk Factors: Obesity, estrogen therapy, PCOS, diabetes.
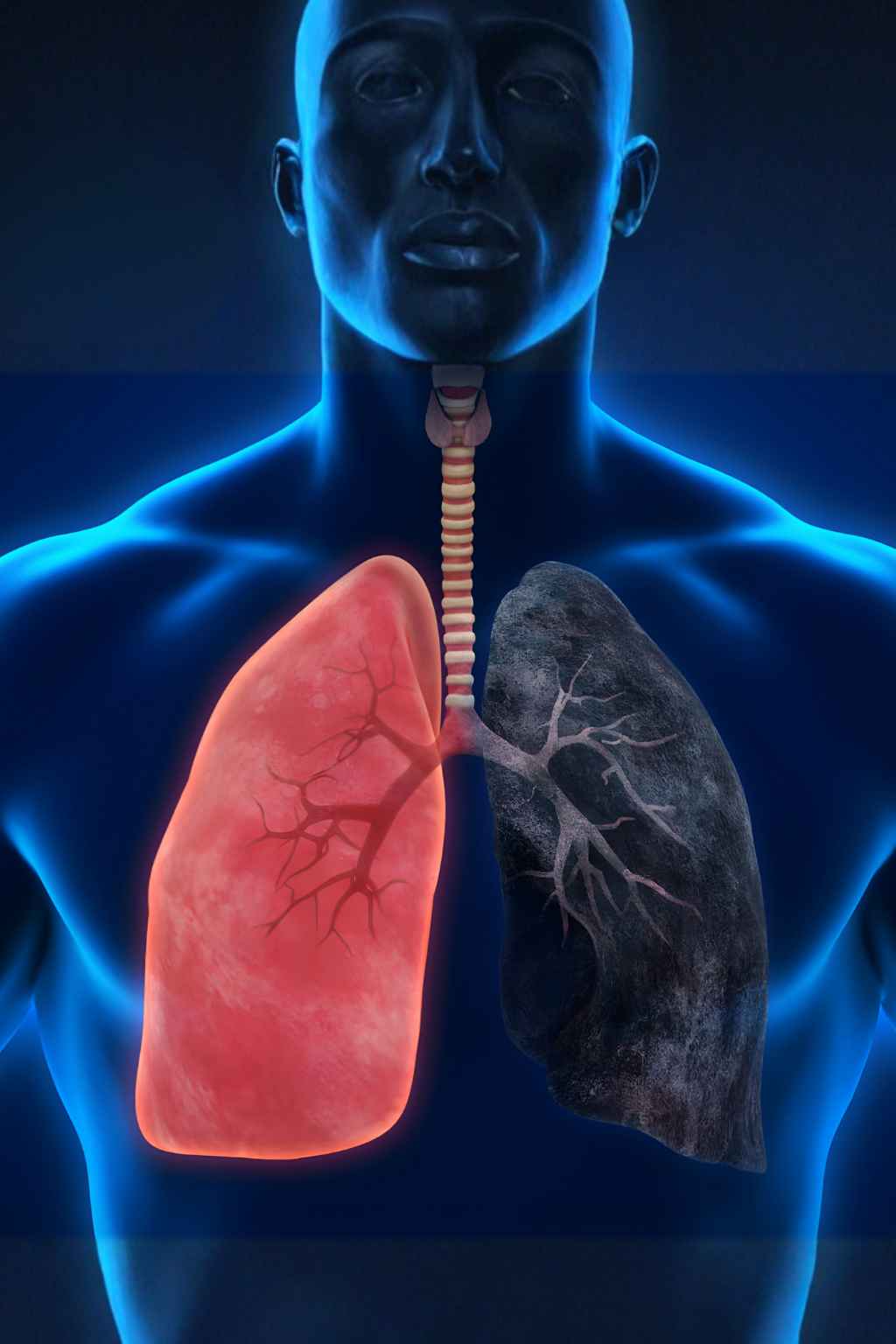
5. Lung Cancer
- Rising concern among women, especially non-smokers.
- Symptoms: Persistent cough, chest pain, hoarseness, breathlessness.
- Risk Factors: Smoking, passive smoke, radon exposure.
6. Colorectal Cancer
- Increasing in young women.
- Symptoms: Blood in stool, changes in bowel habits, weight loss.
- Screening: Colonoscopy starting at age 45 or earlier if family history exists.
Most Common Cancers in Women

1. Breast Cancer
- Overview: Most frequently diagnosed cancer in women globally.
- Symptoms: Breast lump, nipple inversion/discharge, skin changes.
- Risk Factors: Age, family history (BRCA1/2), obesity, alcohol use, HRT.

2. Cervical Cancer
- Cause: Mostly by persistent high-risk HPV infection.
- Symptoms: Abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain, foul-smelling discharge.
- Prevention: HPV vaccination (ages 9–26), Pap smear every 3 years, HPV DNA testing.

3. Ovarian Cancer
- Symptoms: Bloating, abdominal pain, early satiety, urinary urgency.
- Challenges: Often diagnosed late due to non-specific symptoms.
- Risk Factors: Family history, endometriosis, BRCA mutations.

4. Endometrial (Uterine) Cancer
- Symptoms: Postmenopausal bleeding, pelvic discomfort.
- Risk Factors: Obesity, estrogen therapy, PCOS, diabetes.

5. Lung Cancer
- Rising concern among women, especially non-smokers.
- Symptoms: Persistent cough, chest pain, hoarseness, breathlessness.
- Risk Factors: Smoking, passive smoke, radon exposure.

6. Colorectal Cancer
- Increasing in young women.
- Symptoms: Blood in stool, changes in bowel habits, weight loss.
- Screening: Colonoscopy starting at age 45 or earlier if family history exists.
Emotional & Mental Health in Women with Cancer
Women often face unique challenges:
- Fertility concerns
- Body image post-surgery (mastectomy, hysterectomy)
- Menopause-related effects of treatment
- Family, caregiving burdens
Support systems, counseling, support groups and survivorship programs are critical in recovery and quality of life.
Lifestyle Tips to Lower Cancer Risk
- Eat a balanced diet (high in fiber, antioxidants, low in red meat).
- Maintain a healthy weight and stay physically active.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol.
- Breastfeed (protective against breast and ovarian cancers).
- Stay updated with regular check-ups.
Emerging Trends in Women’s Oncology
- Liquid biopsies for early detection
- Targeted therapy and immunotherapy in gynecologic cancers
- Fertility preservation techniques
- AI and genetic profiling for risk prediction
- Survivorship care plans
When to See a Doctor
Don’t ignore:
- Any abnormal bleeding
- Persistent pain or lumps
- Unexplained weight loss
- Changes in bathroom habits
- Breast or pelvic abnormalities
- Early diagnosis saves lives.
- Prevention & Screening Strategy
Breast Cancer
Screening Test: Mammogram
Recommended Age: 40+
Frequency: Every 1–2 years
Cervical Cancer
Screening Test: Pap + HPV test
Recommended Age: 21–65
Frequency: Every 3–5 years
Colorectal Cancer
Screening Test: Colonoscopy
Recommended Age: 45+
Frequency: Every 10 years
Ovarian Cancer
Screening Test: Not routine
Recommended Age: High-risk only
Frequency: Individualized
Breast Cancer
Screening Test: Low-dose CT
Recommended Age: 50–80 (high risk)
Frequency: Yearly
- Female-Specific Risk Factors
- Hormonal influences: Estrogen & progesterone play roles in breast and uterine cancer.
- Reproductive history: Late menopause, nulliparity and infertility can increase risks.
- HPV infection: Affects cervical, vulvar, anal and oropharyngeal cancers.
- Genetic predispositions: BRCA1/2, Lynch syndrome.
- Role of Vaccination
HPV Vaccine:
- Protects against cervical, vaginal, vulvar, anal and oropharyngeal cancers. Best given before sexual debut (ages 9–14).
Hepatitis B Vaccine:
- Prevents liver cancer, relevant to both men and women.
- Conclusion
Cancer in women is not just a disease, it’s a call for proactive care, education and empowerment. With modern screening tools, vaccines, awareness and advanced treatments, most cancers in women are preventable or highly treatable if detected early.
Let’s break the stigma, encourage regular check-ups and support one another. Because every woman deserves a healthy, cancer-free life.
Frequently Asked Questions
The most common are:
Breast cancer
Cervical cancer
Ovarian cancer
Uterine (Endometrial) cancer
Vulvar & Vaginal cancers
Breast lump or nipple discharge
Abnormal vaginal bleeding
Pelvic or abdominal pain
Unexplained weight loss
Persistent bloating
Changes in breast shape/skin
Post-menopausal bleeding
If symptoms persist for more than 2–3 weeks, get checked.
Screening tests include:
Breast cancer: Mammogram (40+), Breast self-exam monthly
Cervical cancer: Pap smear & HPV test every 3–5 years
Ovarian & uterine cancer: Ultrasound if high-risk or symptomatic
Yes — early detection leads to excellent cure rates, especially for breast and cervical cancers.
Some cancers run in families (like breast/ovarian cancer due to BRCA genes).
If you have a strong family history, genetic counselling may help.
Regular exercise
Healthy weight
Avoid smoking & alcohol
Balanced diet (fruits, vegetables, whole grains)
Breastfeeding (reduces breast cancer risk)
Maintaining sexual hygiene
Disclaimer: Results and patient experiences may vary. These are dependent on a number of factors including age, medical history, lifestyle and more.
